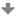Súčet a rozdiel goniometrických funkcií, súčtové vzorce
Pri tomto type úloh využívame vzorce pre (súčet a rozdiel goniometrických funkcií, súčtové vzorce). Zároveň sa predpokladá znalosť predchádzajúcich typov úloh.
- Príklad 1
- Riešte goniometrickú rovnicu s neznámou x \in \mathbb{R}:
\sin (5x + 45^\circ) = \sin x
Riešenie
\sin (5x + 45^\circ)- \sin x = 0 (Využijeme {\pi \over 2} = 90^\circ \Rightarrow 45^\circ = {\pi \over 4}.)
2\cos {\Large 5x + {\pi \over 4} + x \over \Large 2}\sin {\Large 5x + {\pi \over 4} - x \over \Large 2} = 0 (Použili sme vzorec pre \sin x - \sin y.)
2\cos {\Large 6x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2}\sin {\Large 4x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = 0
Využijeme vlastnosť, kedy sa súčin rovná nule (aspoň, keď jeden činiteľ je rovný nule).
2\cos {\Large 6x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2}\sin {\Large 4x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = 0 \Leftrightarrow 2\cos {\Large 6x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = 0 \vee \sin {\Large 4x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = 0
Prvá možnosť:
2\cos {\Large 6x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = 0
Po úprave dostaneme:
\cos {\Large 6x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = 0
Zavedieme substitúciu:
{\Large 6x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = y
\cos y = 0
Z grafu a z tabuľkových hodnôt funkcie kosínus plynie, že \cos y = 0 \Rightarrow y = {\pi \over 2} + k\pi, k \in \mathbb{Z}.
Vrátime sa k substitúcií a upravíme rovnicu:
{\Large 6x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = {\pi \over 2} + k\pi
6x + {\pi \over 4} = \pi + 2k\pi
x_1 = {\pi \over 8} + k {\pi \over 3}, k \in \mathbb{Z} (Prvé riešenie príkladu.)
Druhá možnosť:
\sin {\Large 4x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = 0
Zavedieme substitúciu:
{\Large 4x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = y
\sin y = 0
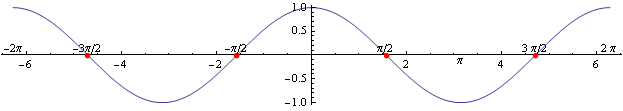
Z grafu a z tabuľkových hodnôt funkcie sínus plynie, že \sin y = 0 \Rightarrow y = k\pi, k \in \mathbb{Z}.
Vrátime sa k substitúcií a upravíme rovnicu:
{\Large 4x + {\pi \over 4} \over \Large 2} = k\pi
4x + {\pi \over 4} = 2k\pi
x_2 = {15\pi \over 16 } + k {\pi \over 2}, k \in \mathbb{Z} (Druhé riešenie príkladu.)
Výsledné riešenie zapíšeme v tvare K = \bigcup\limits_{k\in\mathbb{Z}}\{\frac{\pi}{8}+k{\pi \over 3}; \frac{15}{16}{\pi}+ k {\pi \over 2} \}\;.
- Príklad 2
- Riešte goniometrickú rovnicu s neznámou x \in \mathbb{R}:
-\cos 3x = \cos 7x
Riešenie
\cos 7x + \cos 3x = 0
2\cos {\Large 7x + 3x \over \Large 2}\cos {\Large 7x - 3x \over \Large 2} = 0 (Použili sme vzorec pre \cos x + \cos y.)
2\cos 5x \cos 2x = 0
Využijeme vlastnosť, kedy sa súčin rovná nule (aspoň, keď jeden činiteľ je rovný nule).
2\cos 5x \cos 2x = 0 \Leftrightarrow \cos 5x = 0 \vee \cos 2x = 0
Prvá možnosť:
\cos 5x = 0
Zavedieme substitúciu:
5x = y
\cos y = 0

Z grafu a z tabuľkových hodnôt funkcie kosínus plynie, že \cos y = 0 \Rightarrow y = {\pi \over 2} + k\pi, k \in \mathbb{Z}.
Vrátime sa k substitúcií a upravíme rovnicu:
5x = {\Large \pi \over \Large 2} + k\pi
x_1 = {\Large \pi \over \Large 10} + k{\Large \pi \over \Large 5}, k \in \mathbb{Z} (Prvé riešenie príkladu.)
Druhá možnosť:
\cos 2x = 0
Zavedieme substitúciu:
2x = y
\cos y = 0

Z grafu a z tabuľkových hodnôt funkcie kosínus plynie, že \cos y = 0 \Rightarrow y = {\pi \over 2} + k\pi, k \in \mathbb{Z}.
Vrátime sa k substitúcií a upravíme rovnicu:
2x = {\Large \pi \over \Large 2} + k\pi
x_2 = {\Large \pi \over \Large 4} + k{\Large \pi \over \Large 2}, k \in \mathbb{Z} (Druhé riešenie príkladu.)
Výsledné riešenie zapíšeme v tvare K = \bigcup\limits_{k\in\mathbb{Z}}\{\frac{\pi}{10}+k{\pi \over 5}; \frac{\pi}{4} + k {\pi \over 2} \}\;.
- Príklad 3
- Riešte goniometrickú rovnicu s neznámou x \in \mathbb{R}:
\sin \left(x + {\Large \pi \over \Large 4}\right) = 5\cos \left(x - {\Large \pi \over \Large 4}\right)
Riešenie
\sin x \cos {\Large \pi \over \Large 4} + \cos x \sin {\Large \pi \over \Large 4} = 5 \left (\cos x \cos {\Large \pi \over \Large 4} + \sin x \sin {\Large \pi \over \Large 4} \right) (Použili sme vzorce pre \sin (x+y), \cos (x+y).)
{\sqrt {2} \over 2 }\sin x + {\sqrt {2} \over 2 }\cos x = 5{\sqrt {2} \over 2 }(\cos x + \sin x) (Použili sme tabuľkové hodnoty funkcie (sínus a kosínus).)
{\sqrt {2} \over 2 }(\sin x + \cos x) = 5{\sqrt {2} \over 2 }(\cos x + \sin x)
0 = 5{\sqrt {2} \over 2 }(\cos x + \sin x) - {\sqrt {2} \over 2 }(\sin x + \cos x)
0 = 4{\sqrt {2} \over 2 }(\cos x + \sin x)
2 \sqrt {2}(\cos x + \sin x) = 0
Využijeme vlastnosť, kedy sa súčin rovná nule (aspoň, keď jeden činiteľ je rovný nule).
2 \sqrt {2}(\cos x + \sin x) = 0 \Leftrightarrow \sin x + \cos x = 0
Riešime teda rovnicu:
\sin x + \cos x = 0
\sin x = -\cos x
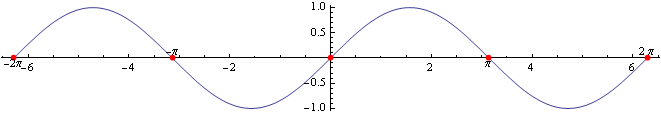
Z grafu oboch funkcií sínus a kosínus plynie:
x = {3 \over 4 }\pi + k\pi, k \in \mathbb{Z} (Využívame periodičnosť goniometrických funkcií.)
Výsledné riešenie zapíšeme v tvare K = \bigcup\limits_{k\in\mathbb{Z}}\{\frac{3\pi}{4}+k\pi \}\;.